Abstract
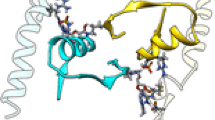
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) (EC.2.4.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of N-ribosidic bonds of the purine ribonucleosides and 2-deoxyribonucleosides in the presence of inorganic orthophosphate as a second substrate. This enzyme is involved in purine-salvage pathway and has been proposed as a promising target for design and development of antimalarial and antibacterial drugs. Recent elucidation of the three-dimensional structure of PNP by X-ray protein crystallography left open the possibility of structure-based virtual screening initiatives in combination with molecular dynamics simulations focused on identification of potential new antimalarial drugs. Most of the previously published molecular dynamics simulations of PNP were carried out on human PNP, a trimeric PNP. The present article describes for the first time molecular dynamics simulations of hexameric PNP from Plasmodium falciparum (PfPNP). Two systems were simulated in the present work, PfPNP in ligand free form, and in complex with immucillin and sulfate. Based on the dynamical behavior of both systems the main results related to structural stability and protein-drug interactions are discussed.

Purine nucleoside phosphorylase is a potential target for the development of antibacterial and antimalarial drugs. Molecular dynamics simulations have been performed to evaluate the structural and dynamical properties of PfPNP. Two systems were simulated, the protein in the apo form and a second system for the ternary complex involving PfPNP, SO4, and an inhibitor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilles HM (2002) In: Warrell DA, Gilles HM (eds) Essential Malariology. Arnold, New York, pp 1–7
World Health Organization (2007) Malaria, Fact Sheet No. 94. Geneva, Switzerland
Suh KN, Kain KC, Keystone JS (2004) Malaria. Can Med Assoc J 170:1693–1702
Sachs JD (2002) A new global effort to control malaria. Science 298:122–124
Wellems TE (2002) Plasmodium chloroquine resistance and the search for a replacement antimalarial drug. Science 298:124–125
Hassan HF, Coombs GH (1988) Purine and pyrimidine metabolism in parasitic protozoa. FEMS Microbiol Rev 4:47–83
Asahi H, Kanazawa T, Kajihara Y, Takahashi K, Takahashi T (1996) Hypoxanthine: a low molecular weight factor essential for growth of erythrocytic Plasmodium falciparum in a serum-free medium. Parasitology 113:19–23
Kicska GA, Tyler PC, Evans GB, Furneaux RH, Kim K, Schramm VL (2002) Transition state analogue inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem 277:3219–3225
Kicska GA, Tyler PC, Evans GB, Furneaux RH, Schramm VL, Kim K (2002) Purine-less death in Plasmodium falciparum induced by immucillin-H, a transition state analogue of purine nucleoside phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 277:3226–3231
Ting LM, Shi W, Lewandowicz A, Singh V, Mwakingwe A, Birck MR, Ringia EA, Bench G, Madrid DC, Tyler PC, Evans GB, Furneaux RH, Schramm VL, Kim K (2005) Targeting a novel Plasmodium falciparum purine recycling pathway with specific immucillins. J Bio Chem 280:9547–9554
Schnick C, Robien MA, Brzozowski AM, Dodson EJ, Murshudov GB, Anderson L, Luft, Mehlin C, Hol WGJ, Brannigan JA, Wilkinson AJ (2005) Structures of Plasmodium falciparum purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with sulfate and its natural substrate inosine. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61:1245–1254
Shi W, Ting LM, Kicska GA, Lewandowicz A, Tyler PC, Evans GB, Furneaux RH, Kim K, Almo SC, Schramm VL (2004) Plasmodium falciparum purine nucleoside phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 279:18103–18106
Berman HM, Battistuz T, Bhat TN, Bluhm WF, Bourne PE, Burkhardt K, Feng Z, Gilliland GL, Iype L, Jain S, Fagan P, Marvin J, Padilla D, Ravichandran V, Schneider B, Thanki N, Weissig H, Westbrook JD, Zardecki C (2002) The Protein Data Bank. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:899–907
van der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, Groenhof G, Mark AE, Berendsen HJC (2005) GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. J Comp Chem 26:1701–1718 http://www.gromacs.org
Ooestenbrink C, Soares TA, van der Vegt NF, van Gunsteren WF (2005) Validation of the 53A6 GROMOS force field. Eur Biophys J 34:273–284
van Aalten DM, Bywater B, Findlay JB, Hendlich M, Hooft RW, Vriend G (1996) PRODRG, a program for generating molecular topologies and unique molecular descriptors from coordinates of small molecules. Comput Aided Mol Des 10:255–262 http://davapc1.bioch.dundee.ac.uk/programs/prodrg/prodrg.html
Schmidt MW, Baldridge KK, Boatz JA, Elbert ST, Gordon MS, Jensen JH, Koseki S, Matsunaga N, Nguyen KA, Su S, Windus TL, Dupuis M, Montgomery JA (1993) General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J Comput Chem 14:1347–1363
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, Hermans J (1981) Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration. In: Pullman B (ed) Intermolecular forces. Reidel D Publishing Company Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 331–342
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJC, Fraaije JGEM (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18:1463–1472
Miyamoto S, Kollman PA (1992) Absolute and relative binding free energy calculations of the interaction of biotin and its analogs with streptavidin using molecular dynamics/free energy perturbation approaches. J Comput Chem 16:226–245
Chowdhuri S, Tan ML, Ichiye T (2006) Dynamical properties of the soft sticky dipole-quadrupole-octupole water model: a molecular dynamics study. J Chem Phys 125:144513
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle Mesh Ewald - an n.log(n) method for ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98:10089–10092
Timmers LFSM, Caceres RA, Vivan AL, Gava LM, Dias R, Ducati RG, Basso LA, Santos DS, de Azevedo WF (2008) Structural studies of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase: towards a new specific empirical scoring function. Arch Biochem Biophys 479:28–38
Silva RG, Nunes JE, Canduri F, Borges JC, Gava LM, Moreno FB, Basso LA, Santos DS (2007) Purine nucleoside phosphorylase: a potential target for the development of drugs to treat T-cell- and apicomplexan parasite-mediated diseases. Curr Drugs Target 8:413–422
de Azevedo WF Jr, Canduri F, dos Santos DM, Silva RG, de Oliveira JS, de Carvalho LPS, Basso LA, Mendes MA, Palma MS, Santos DS (2003) Crystal structure of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase at 2.3 Å resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:545–552
Caceres RA, Saraiva Timmers LF, Dias R, Basso LA, Santos DS, de Azevedo WF (2008) Molecular modeling and dynamics simulations of PNP from Streptococcus agalactiae. Bioorg Med Chem 16:4984–4993
Timmers LFSM, Caceres RA, Basso LA, Santos DS, de Azevedo Jr. WF (2008) Structural Bioinformatics Study of PNP from Listeria monocytogenes. Protein Pep Lett 15:843–849
de Azevedo WF Jr, Canduri F, dos Santos DM, Pereira JH, Dias MVB, Silva RG, Mendes MA, Basso LA, Palma MS, Santos DS (2003) Structural basis for inhibition of human PNP by immucillin-H. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:917
Canduri F, Fadel V, Basso LA, Palma MS, Santos DS, de Azevedo WF (2005) New catalytic mechanism for human purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:646–649
Santos DM, Canduri F, Pereira JH, Dias MVB, Silva RG, Mendes MA, Palma MS, Basso LA, de Azevedo WF, Santos DS (2003) Crystal structure of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with acyclovir. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:553–559
de Azevedo WF, Canduri F, dos Santos DM, Pereira JH, Dias MVB, Silva RG, Mendes MA, Basso LA, Palma MS, Santos DS (2003) Crystal structure of human PNP complexed with guanine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:767–772
Silva RG, Pereira JH, Canduri F, de Azevedo WF, Basso LA, Santos DS (2005) Kinetics and crystal structure of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase in complex with 7-methyl-6-thio-guanosine. Arch Biochem Biophys 442:49–58
Canduri F, dos Santos DM, Silva RG, Mendes MA, Basso LA, Palma MS, de Azevedo WF, Santos DS (2004) Structures of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with inosine and ddI. Biochem Biophys Res Comum 313:907–914
Canduri F, Silva RG, dos Santos DM, Palma MS, Basso LA, Santos DS, de Azevedo WF(2005) Structure of human PNP complexed with ligands. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61:856–862
Nolasco DO, Canduri F, Pereira JH, Cortinóz, Palma MS, Oliveira JS, Basso LA, de Azevedo WF, Santos DS (2004) Crystallographic structure of PNP from Mycobacterium tuberculosis at 1.9 Å resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Comum 324:789–794
de Azevedo WF, Dias R (2008) Computational methods for calculation of ligand-binding affinity. Curr Drug Targets 9:1031–1039
de Azevedo WF (2008) Protein-drug interactions. Curr Drug Targets 9:1030–1030
Dias R, de Azevedo WF (2008) Molecular docking algorithms. Curr Drug Targets 9:1040–1047
Canduri F, de Azevedo WF (2008) Protein crystallography in drug discovery. Curr Drug Targets 9:1048–1053
Pauli I, Timmers LFSM, Caceres RA, Soares MBP, de Azevedo WF (2008) In silico and in vitro. Identifying new drugs. Curr Drug Targets 9:1054–1061
Dias R, Timmers LFSM, Caceres RA, de Azevedo WF (2008) Evaluation of molecular docking using polynomial empirical scoring functions. Curr Drug Targets 9:1062–1070
de Azevedo WF, Dias R (2008) Experimental approaches to evaluate the thermodynamics of protein-drug interactions. Curr Drug Targets 9:1071–1076
Caceres RA, Pauli I, Timmers LFSM, de Azevedo WF (2008) Molecular recognition models: a challenge to overcome. Curr Drug Targets 9:1077–1083
Barcellos GB, Pauli I, Caceres RA, Timmers LFSM, Dias R, de Azevedo WF (2008) Molecular modeling as tool for drug discovery. Curr Drug Targets 9:1084–1091
Timmers LFSM, Pauli I, Caceres RA, de Azevedo WF (2008) Drug-binding databases. Curr Drug Targets 9:1092–1099
de Azevedo WF , Canduri F, Fadel V, Teodoro LG, Hial V, Gomes RA (2001) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 287:277–281
de Azevedo WF (2007) Editorial. Current Drug Targets 8:387–387
Canduri F, Perez PC, Caceres RA, de Azevedo WF (2007) Protein kinases as targets for antiparasitic chemotherapy drugs. Curr Drug Targets 8:389–398
Marques MR, Pereira JH, Oliveira JS, Basso LA, Santos DS, de Azevedo WF , Palma MS (2007) The inhibition of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase as a model for development of novel antimicrobials. Curr Drug Targets 8:445–457
Dias MVB, Ely F, Palma MS, de Azevedo WF, Basso LA, Santos DS (2007) Chorismate synthase: an attractive target for drug development against orphan diseases. Curr Drug Targets 8:437–444
Pereira JH, Vasconcelos IB, Oliveira JS, Caceres RA, de Azevedo WF , Basso LA, Santos DS (2007) Shikimate kinase: a potential target for development of novel antitubercular. Curr Drug Targets 8:459–468
de Amorim HLN, Caceres RA, Netz PA (2008) Linear Interaction Energy (LIE) method in lead discovery and optimization. Curr Drug Targets 9:1100–1105
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Pesquisas, Brazil), CAPES and Instituto do Milênio (CNPq-MCT). RAC would like to thank CNPq for the fellowship. WFA and RGS are senior researchers of CNPq
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. B. Z and R. A. C. contributed equally to this work, the order of authorship being arbitrary.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanchi, F.B., Caceres, R.A., Stabeli, R.G. et al. Molecular dynamics studies of a hexameric purine nucleoside phosphorylase. J Mol Model 16, 543–550 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-009-0557-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-009-0557-3