Abstract
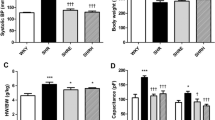
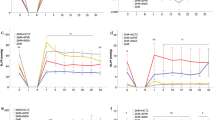
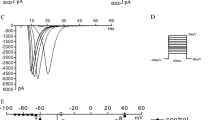
Brief periods (a few seconds) of cyclic coronary occlusions applied early in reperfusion induce a cardioprotection against infarct size, called postconditioning (PostC) in which B2-bradykinin receptors play a pivotal role. Since angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors reduce degradation of kinins, we studied the effects of PostC on infarct size and postischemic myocardial dysfunction in both normotensive (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) acutely or chronically treated with the ACE inhibitor Captopril. Isolated hearts from SHR and WKY rats were subjected to the following protocols: (a) ischemia for 30- and 120-min reperfusion (I/R); (b) I/R + PostC protocol (5-cycles 10-s I/R); (c) pretreatment with Captopril for 4-weeks before to subject the hearts to I/R with or without PostC maneuvers. Some SHR hearts were treated with Captopril during the 20- or 40-min early reperfusion with or without PostC maneuvers. Cardiac function was assessed in vivo with echocardiography. Left ventricular pressure and infarct size were measured ex vivo. Chronic Captopril significantly reduced left ventricular hypertrophy in SHR, and reduced infarct size in both WKY and SHR hearts. PostC maneuvers significantly reduced infarct size in WKY, but not in SHR hearts. Yet, PostC slightly improved postischemic systolic function in untreated SHR. Captopril given in reperfusion was unable to limit I/R injury in SHR hearts. Data show that PostC protection against infarct size is blunted in SHR and that PostC is unable to add its protective effect to those of chronic Captopril, which per se reduces cardiac hypertrophy and heart susceptibility to I/R insult.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benter IF, Yousif MH, Anim JT, Cojocel C, Diz DI (2006) Angiotensin-(1-7) prevents development of severe hypertension and end-organ damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats treated with L-NAME. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H684–H691
Benzing T, Fleming I, Blaukat A, Müller-Esterl W, Busse R (1999) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ramiprilat interferes with the sequestration of the B2 kinin receptor within the plasma membrane of native endothelial cells. Circulation 99:2034–2040
Boengler K, Buechert A, Heinen Y, Roeskes C, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Heusch G, Schulz R (2008) Cardioprotection by ischemic postconditioning is lost in aged and STAT3-deficient mice. Circ Res 102:131–135
Boengler K, Schulz R, Heusch G (2009) Loss of cardioprotection with ageing. Cardiovasc Res 83:247–261
Cohen MV, Yang XM, Liu GS, Heusch G, Downey JM (2001) Acetylcholine, bradykinin, opioids, and phenylephrine, but not adenosine, trigger preconditioning by generating free radicals and opening mitochondrial KATP channels. Circ Res 89:273–278
Das DK, Maulik N, Engelman RM (2004) Redox regulation of angiotensin II signaling in the heart. J Cell Mol Med 8:144–152
Delles C, Schneider MP, John S, Gekle M, Schmieder RE (2002) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II AT1-receptor blockade reduce the levels of asymmetrical N(G), N(G)-dimethylarginine in human essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 15:590–593
Ebrahim Z, Yellon DM, Baxter GF (2007) Ischemic preconditioning is lost in aging hypertensive rat heart: independent effects of aging and longstanding hypertension. Exp Gerontol 42:807–814
Evangelista S, Manzini S (2005) Antioxidant and cardioprotective properties of the sulphydryl angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor zofenopril. The J of Intern Med Res 33:42–54
Fantinelli JC, Mosca SM (2007) Comparative effects of ischemic pre and postconditioning on ischemia-reperfusion injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Mol Cell Biochem 296:45–51
Ferdinandy P, Schulz R, Baxter GF (2007) Interaction of cardiovascular risk factors with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, preconditioning, and postconditioning. Pharmacol Rev 59:418–458
Fiordaliso F, Cuccovillo I, Bianchi R, Bai A, Doni M, Salio M, De Angelis N, Ghezzi P, Latini R, Masson S (2006) Cardiovascular oxidative stress is reduced by an ACE inhibitor in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Life Sci 79:121–129
Flather MD, Yusuf S, Køber L, Pfeffer M, Hall A, Murray G, Torp-Pedersen C, Ball S, Pogue J, Moyé L, Braunwald E (2000) Long-term ACE-inhibitor therapy in patients with heart failure or left-ventricular dysfunction: a systematic overview of data from individual patients. ACE-Inhibitor Myocardial Infarction Collaborative Group. Lancet 355:1575–1581
Fleming I (2006) Signaling by the angiotensin-converting enzyme. Circ Res 98:887–896
Gardin JM, Siri F, Kitsis RN, Leinwand L (1996) Intravascular ultrasound catheter evaluation of the left ventricle in mice: a feasibility study. Echocardiography 13:609–612
Granfeldt A, Lefer DJ, Vinten-Johansen J (2009) Protective ischemia in patients: preconditioning and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Res 83:234–246
Hausenloy DJ, Ong SB, Yellon DM (2009) The mitochondrial permeability transition pore as a target for preconditioning and postconditioning. Basic Res Cardiol 104:189–202
Hausenloy DJ, Tsang A, Yellon DM (2005) The reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway: a common target for both ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Trends Cardiovasc Med 15:69–75
Heusch G (2004) Postconditioning: old wine in a new bottle? J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1111–1112
Heusch G, Boengler K, Schulz R (2008) Cardioprotection: nitric oxide, protein kinases, and mitochondria. Circulation 118:1915–1919
Hilgenfeldt U, Stannek C, Lukasova M, Schnolzer M, Lewicka S (2005) Rat tissue kallikrein releases a kallidin-like peptide from rat low-molecular-weight kininogen. Br J Pharmacol 146:958–963
Iliodromitis EK, Downey JM, Heusch G, Kremastinos DT (2009) What is the optimal postconditioning algorithm? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 14:269–273
Kin H, Zatta AJ, Lofye MT, Amerson BS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F, Zhao ZQ, Guyton RA, Headrick JP, Vinten-Johansen J (2005) Postconditioning reduces infarct size via adenosine receptor activation by endogenous adenosine. Cardiovasc Res 67:124–133
Kohlstedt K, Brandes RP, Muller-Esterl W, Busse R, Fleming I (2004) Angiotensin-converting enzyme is involved in outside-in signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 94:60–67
Liu X, Lukasova M, Zubakova R, Lewicka S, Hilgenfeldt U (2005) A kallidin-like peptide is a protective cardiac kinin, released by ischaemic preconditioning of rat heart. Br J Pharmacol 146:952–927
Liu X, Lukasova M, Zubakova R, Lewicka S, Hilgenfeldt U (2006) Kallidin-like peptide mediates the cardioprotective effect of the ACE inhibitor captopril against ischaemic reperfusion injury of rat heart. Br J Pharmacol 148:825–832
Ludbrook J (1994) Repeated measurements and multiple comparison in cardiovascular research. Cardiovasc Res 28:301–311
Marktanner R, Nacke P, Feindt P, Hohlfeld T, Schipke JD, Gams E (2006) Delayed preconditioning via Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition: pros and cons from an experimental study. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33:787–792
Miura T, Miki T (2008) Limitation of myocardial infarct size in the clinical setting: current status and challenges in translating animal experiments into clinical therapy. Basic Res Cardiol 103:501–513
Morris SD, Yellon DM (1997) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors potentiate preconditioning through bradykinin B2 receptor activation in human heart. J Am Coll Cardiol 29:1599–1606
Norton GR, Veliotes DG, Osadchii O, Woodiwiss AJ, Thomas DP (2008) Susceptibility to systolic dysfunction in the myocardium from chronically infarcted spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H372–H378
Oldenburg O, Qin Q, Krieg T, Yang XM, Philipp S, Critz SD, Cohen MV, Downey JM (2004) Bradykinin induces mitochondrial ROS generation via NO, cGMP, PKG, and mitoKATP channel opening and leads to cardioprotection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H468–H476
Oldenburg O, Qin Q, Sharma AR, Cohen MV, Downey JM, Benoit JN (2002) Acetylcholine leads to free radical production dependent on KATP channels, Gi proteins, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and tyrosine kinase. Cardiovasc Res 55:544–552
Pagliaro P, Mancardi D, Rastaldo R, Penna C, Gattullo D, Miranda KM, Feelisch M, Wink DA, Kass DA, Paolocci N (2003) Nitroxyl affords thiol-sensitive myocardial protective effects akin to early preconditioning. Free Radic Biol Med 34:33–43
Pagliaro P, Penna C (2005) Rethinking the renin-angiotensin system and its role in cardiovascular regulation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 19:77–87
Papaioannou VE, Fox JG (1993) Efficacy of tribromoethanol anesthesia in mice. Lab Anim Sci 43:189–192
Peart JN, Gross ER, Reichelt ME, Hsu A, Headrick JP, Gross GJ (2008) Activation of kappa-opioid receptors at reperfusion affords cardioprotection in both rat and mouse hearts. Basic Res Cardiol 103:454–463
Penna C, Cappello S, Mancardi D, Raimondo S, Rastaldo R, Gattullo D, Losano G, Pagliaro P (2006) Post-conditioning reduces infarct size in the isolated rat heart: role of coronary flow and pressure and the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway. Basic Res Cardiol 101:168–179
Penna C, Mancardi D, Raimondo S, Geuna S, Pagliaro P (2008) The paradigm of postconditioning to protect the heart. J Cell Mol Med 12:435–458
Penna C, Mancardi D, Rastaldo R, Losano G, Pagliaro P (2007) Intermittent activation of bradykinin B2 receptors and mitochondrial KATP channels trigger cardiac postconditioning through redox signaling. Cardiovasc Res 75:168–177
Penna C, Mancardi D, Rastaldo R, Pagliaro P (2009) Cardioprotection: a radical view Free radicals in pre and postconditioning. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:781–793
Penna C, Mancardi D, Tullio F, Pagliaro P (2008) Postconditioning and intermittent bradykinin induced cardioprotection require cyclooxygenase activation and prostacyclin release during reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 103:368–377
Penna C, Mancardi D, Tullio F, Pagliaro P (2009) Intermittent adenosine at the beginning of reperfusion does not trigger cardioprotection. J Surg Res 153:231–238
Penna C, Mognetti B, Tullio F, Gattullo D, Mancardi D, Moro F, Pagliaro P, Alloatti G (2009) Post-ischaemic activation of kinases in the pre-conditioning-like cardioprotective effect of the platelet-activating factor. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 197:175–185
Penna C, Mognetti B, Tullio F, Gattullo D, Mancardi D, Pagliaro P, Alloatti G (2008) The platelet activating factor triggers preconditioning-like cardioprotective effect via mitochondrial K-ATP channels and redox-sensible signaling. J Physiol Pharmacol 59:47–54
Penna C, Perrelli MG, Raimondo S, Tullio F, Merlino A, Moro F, Geuna S, Mancardi D, Pagliaro P (2009) Postconditioning induces an anti-apoptotic effect and preserves mitochondrial integrity in isolated rat hearts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:794–801
Penna C, Rastaldo R, Mancardi D, Raimondo S, Cappello S, Gattullo D, Losano G, Pagliaro P (2006) Post-conditioning induced cardioprotection requires signaling through a redox-sensitive mechanism, mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K + channel and protein kinase C activation. Basic Res Cardiol 101:180–189
Penna C, Tullio F, Merlino A, Moro F, Raimondo S, Rastaldo R, Perrelli MG, Mancardi D, Pagliaro P (2009) Postconditioning cardioprotection against infarct size and post-ischemic systolic dysfunction is influenced by gender. Basic Res Cardiol 104:390–402
Pfeffer JM, Pfeffer MA, Mirsky I, Braunwald E (1982) Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy and prevention of left ventricular dysfunction by captopril in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:3310–3314
Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E, Moyé LA, Basta L, Brown EJ Jr, Cuddy TE, Davis BR, Geltman EM, Goldman S, Flaker GC et al (1992) Effect of captopril on mortality and morbidity in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Results of the survival and ventricular enlargement trial. The SAVE Investigators. N Engl J Med 327:669–677
Philipp S, Yang XM, Cui L, Davis AM, Downey JM, Cohen MV (2006) Postconditioning protects rabbit hearts through a protein kinase C-adenosine A2b receptor cascade. Cardiovasc Res 70:308–314
Remme WJ (2003) Should ACE inhibition always be first-line therapy in heart failure? Lessons from the CARMEN Study. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 17:107–109
Schulz R, Post H, Vahlhaus C, Heusch G (1998) Ischemic preconditioning in pigs: a graded phenomenon: its relation to adenosine and bradykinin. Circulation 98:1022–1029
Skyschally A, van Caster P, Iliodromitis EK, Schulz R, Kremastinos DT, Heusch G (2009) Ischemic postconditioning: experimental models and protocol algorithms. Basic Res Cardiol 104:469–483
Staat P, Rioufol G, Piot C, Cottin Y, Cung TT, L’Huillier I, Aupetit JF, Bonnefoy E, Finet G, André-Fouët X, Ovize M (2005) Postconditioning the human heart. Circulation 112:2143–2148
Tsang A, Hausenloy DJ, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM (2004) Postconditioning: a form of “modified reperfusion” protects the myocardium by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway. Circ Res 95:230–232
Wall TM, Sheehy R, Hartman JC (1994) Role of bradykinin in myocardial preconditioning. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:681–689
Weidenbach R, Schulz R, Gres P, Behrends M, Post H, Heusch G (2000) Enhanced reduction of myocardial infarct size by combined ACE inhibition and AT(1)-receptor antagonism. Br J Pharmacol 131:138–144
Xi L, Das A, Zhao ZQ, Merino VF, Bader M, Kukreja RC (2008) Loss of myocardial ischemic postconditioning in adenosine A1 and bradykinin B2 receptors gene knockout mice. Circulation 118:S32–S37
Yang XM, Krieg T, Cui L, Downey JM, Cohen MV (2004) NECA and bradykinin at reperfusion reduce infarction in rabbit hearts by signaling through PI3 K, ERK, and NO. J Mol Cell Cardiol 36:411–421
Yang XM, Proctor JB, Cui L, Krieg T, Downey JM, Cohen MV (2004) Multiple, brief coronary occlusions during early reperfusion protect rabbit hearts by targeting cell signaling pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1103–1110
Yang XP, Liu YH, Scicli GM, Webb CR, Carretero OA (1997) Role of kinins in the cardioprotective effect of preconditioning: study of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in B2 kinin receptor knockout mice and kininogen-deficient rats. Hypertension 30:735–740
Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, Bosch J, Davies R, Dagenais G (2000) Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 342:145–153
Zahler S, Kupatt C, Becker BF (1999) ACE-inhibition attenuates cardiac cell damage and preserves release of NO in the postischemic heart. Immunopharmacology 44:27–33
Zhao HX, Wang XL, Wang YH, Wu Y, Li XY, Lv XP, Zhao ZQ, Zhao RR, Liu HR (2009) Attenuation of myocardial injury by postconditioning: role of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha. Basic Res Cardiol. doi:10.1007/s00395-009-0044-0
Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F, Wang NP, Guyton RA, Vinten-Johansen J (2003) Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H579–H588 (Erratum in: Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2004; 286: H477)
Zhu M, Feng J, Lucchinetti E, Fischer G, Xu L, Pedrazzini T, Schaub MC, Zaugg M (2006) Ischemic postconditioning protects remodeled myocardium via the PI3 K-PKB/Akt reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res 72:152–162
Acknowledgments
The authors were supported by Compagnia di S. Paolo, National Institutes of Cardiovascular Research (INRC, FM, PP); Regione Piemonte (PP), PRIN (PP), ex-60% (CP, PP). The authors wish to thank Prof. Donatella Gattullo for insightful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penna, C., Tullio, F., Moro, F. et al. Effects of a protocol of ischemic postconditioning and/or captopril in hearts of normotensive and hypertensive rats. Basic Res Cardiol 105, 181–192 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-009-0075-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-009-0075-6