Summary
Objective
There is controversy whether new biomarkers are able to identify myocardial ischemia in the absence of myonecrosis.
Method
We measured NT-pro BNP, NT-pro ANP, ischemia-modified albumin (IMA) and placental growth factor (PlGF) in patients undergoing nuclear stress testing for suspected ischemic heart disease. A thallium scan was used for detection of reversible myocardial ischemia and cardiac troponin T (cTnT) for exclusion of stress-induced myonecrosis. Of 195 patients, 24 with reversible and 62 with no perfusion defect were included in the analysis. Plasma levels were measured before, 18 min and 4 h after stress testing.
Results
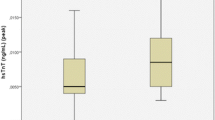
Of the 86 patients, 52 received an exercise stress and 34 dipyridamol. New myonecrosis indicated by cTnT could be excluded in all patients. Plasma levels of NT-pro BNP and NT-pro ANP before testing were significantly higher in patients who later developed reversible perfusion defects (NT-pro BNP 139.00 (58.25/367.01) pg/mL vs 327.45 (120.50/972.85) pg/mL, p < 0.05; NT-pro ANP 732.5 (470.0/ 1220.0) pg/mL vs 1470.0 (694.0/ 1910.0) pg/mL, p < 0.05). Plasma levels of NT-pro BNP, NT-pro ANP and PIGF did not change significantly after stress testing, IMA levels rose significantly after 4 h in patients with and without reversible perfusion defects.
Conclusion
The elevation of NTpro BNP and NT-pro ANP at baseline may represent the cumulative effect of repeated bouts of myocardial ischemia. A single brief episode of provoced ischemia does not cause a significant increase of the measured biomarkers beside from IMA after exercise stress test potentially indicating skeletal muscle ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apple FS, Quist HE, Otto AP, Mathews WE, Murakami MM (2002) Release characteristics of cardiac biomarkers and ischemia-modified albumin as measured by the albumin cobalt- binding test after a marathon race. Clin Chem 48:1097–1100
Borderie D, Allanore Y, Meune C, Devaux JY, Ekindjian OG, Kahan A (2004) High ischemia-modified albumin concentration reflects oxidative stress but not myocardial involvement in systemic sclerosis. Clin Chem 50:2190–2193
Cummins P, Young A, Auckland ML, Michie CA, Stone PCW, Shepstone DJ (1987) Comparison of serum cardiac specific troponin-I with creatine kinase, creatine kinase-MB, tropomyosin, myoglobin, and C-reactive protein release in marathon runners: cardiac or skeletal muscle trauma. Eur J Clin Invest 17:317–324
de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Bentley J H, Omland T, Sabatine MS, McCabe CH, Hall C, Cannon CP, Braunwald E (2001) The prognostic value of Btype natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 345:1014–1021
Edwards SW, Hallett MB, Campbell AK (1984) Oxygen-radical production during inflammation may be limited by oxygen concentration. Biochem J 217:851–854
Fishbein MC, Wang T, Matijasevic M, Hong L, Apple FS (2003) Myocardial tissue troponins T and I. An immunohistochemical study in experimental models of myocardial ischemia. Cardiovasc Pathol 12:65–71
Foote RS, Pearlman JD, Siegel AH, Yeo KT (2004) Detection of exerciseinduced ischemia by changes in Btype natriuretic peptides. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1980–1987
Giannitsis E (2005) Rationale for testing the cardiovascular risk for patients with COX-2 inhibitors on the basis of biomarker NT-proBNP. Clin Lab 51:63–83
Goetze JP, Christoffersen C, Perko M, Arendrup H, Rehfeld JF, Kastrup J, Nielsen LB (2003) Increased cardiac BNP expression associated with myocardial ischemia. FASEB J 17:1105–1107
Heeschen C, Dimmeler S, Fichtlscherer S, Hamm CW, Berger J, Simoons ML, Zeiher AM (2004) CAPTURE Investigators. Prognostic value of placental growth factor in patients with acute chest pain. JAMA 291:435–441
Herrmann M, Scharhag J, Miclea M, Urhausen A, Herrmann W, Kindermann W (2003) Post-race kinetics of cardiac troponin T and I and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in marathon runners. Clin Chem 49:831–834
Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Olschewski M, Kasper W, Hruska N, Jackle S, Binder L (2002) Importance of cardiac troponins I and T in risk stratification of patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 106:1263–1268
Kragelund C, Gronning B, Kober L, Hildebrandt P, Steffensen R (2005) N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term mortality in stable coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 352:666–675
Marumoto K, Hamada M, Hiwada K (1995) Increased secretion of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides during acute myocardial ischaemia induced by dynamic exercise in patients with angina pectoris. Clin Sci 88:551–556
McNairy M, Gardetto N, Clopton P, Garcia A, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Ziegler M, Maisel AS (2002) Stability of B-type natriuretic peptide levels during exercise in patients with congestive heart failure: implications for outpatient monitoring with B-type natriuretic peptide. Am Heart J 143:406–411
Muller-Bardorff M, Weidtmann B, Giannitsis E, Kurowski V, Katus HA (2002) Release Kinetics of Cardiac Troponin T in Survivors of Confirmed Severe Pulmonary Embolism. Clin Chem 48:673–675
Nishimura K, Ban T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Imura H (1990) Atrial pacing stimulates secretion of atrial natriuretic polypeptide without elevation of atrial pressure in awake dogs with experimental complete atrioventricular block. Circ Res 66:115–122
Ohba H, Takada H, Musha H, Nagashima J, Mori N, Awaya T, Omiya K, Murayama M (2001) Effects of prolonged strenuous exercise on plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide in healthy men. Am Heart J 141:751–758
Omland T, Richards AM, Wergeland R, Vik-Mo H (2005) B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term survival in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 95:24–28
Pfister R, Scholz M, Wielckens K, Erdmann E, Schneider C (2004) A Use of NT-proBNP in routine testing and comparison to BNP. Eur J Heart Fail 6:289–293
Roy D, Quiles J, Sharma R, Sinha M, Avanzas P, Gaze D, Kaski JC (2004) Ischemia-modified albumin concentrations in patients with peripheral vascular disease and exercise-induced skeletal muscle ischemia. Clin Chem 50:1656–1660
Roy D, Quiles J, Sinha M, Floros D, Gaze D, Collinson P, Baxter GF, Kaski JC (2004) Effect of radiofrequency catheter ablation on the biochemical marker ischemia modified albumin. Am J Cardiol 94:234–236
Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, Omland T, Desai MY, Tanasijevic M, Hall C, McCabe CH, Braunwald E (2004) Acute changes in circulating natriuretic peptide levels in relation to myocardial ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1988–1995
Sinha MK, Gaze DC, Tippins JR, Collinson PO, Kaski JC (2003) Ischemia modified albumin is a sensitive marker of myocardial ischemia after percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation 107:2403–2405
Sinha MK, Roy D, Gaze DC, Collinson PO, Kaski JC (2004) Role of "Ischemia modified albumin", a new biochemical marker of myocardial ischaemia, in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes. Emerg Med J 21:29–34
Weber M, Dill T, Arnold R, Rau M, Ekinci O, Muller KD, Berkovitsch A, Mitrovic V, Hamm C (2004) N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide predicts extent of coronary artery disease and ischemia in patients with stable angina pectoris. Am Heart J 148:612–620
Wu AH, Smith A, Wieczorek S, Mather JF, Duncan B, White CM, McGill C, Katten D, Heller G (2003) Biological variation for N-terminal pro- and B-type natriuretic peptides and implications for therapeutic monitoring of patients with congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 92:628–631
Yasue H, Yoshimura M, Sumida H, Kikuta K, Kugiyama K, Jougasaki M, Ogawa H, Okumura K, Mukoyama M, Nakao K (1994) Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation 90:195–203
Zapico-Muniz E, Santalo-Bel M, Merce-Muntanola J, Montiel JA, Martinez- Rubio A, Ordonez-Llanos J (2004) Ischemia-modified albumin during skeletal muscle ischemia. Clin Chem 50:1063–1065
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurz, K., Voelker, R., Zdunek, D. et al. Effect of stress-induced reversible ischemia on serum concentrations of ischemia-modified albumin, natriuretic peptides and placental growth factor. Clin Res Cardiol 96, 152–159 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-007-0469-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-007-0469-5