Abstract
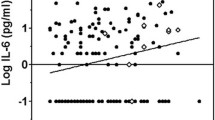
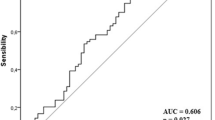
Accumulating evidence suggests that inflammation plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. This recognition has stimulated the evaluation of different inflammatory markers as potential predictors of cardiovascular risk. However, the existing data are limited and controversial. This study was designed to simultaneously measure serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L), metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and to evaluate their ability to predict prognosis. A prospective cohort study was conducted with 263 patients with first STEMI who were admitted to our institute within 6 h of symptoms onset. Clinical data were recorded and serum admission levels of IL-6, sCD40L, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 were measured by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The patients were then followed prospectively for the occurrence of cardiovascular mortality for 3 years. Follow-up information was available for 228 patients (86.7%) from the 263 STEMI patients; 34 patients died from cardiovascular causes during the 3-year follow-up period. Kaplan-Meier plots demonstrated a significant increase in cardiovascular mortality with increasing IL-6 levels (χ2 = 14.13, P = 0.0002, by log-rank test). Logistic regression analysis revealed that IL-6 was an independent predictor for cardiovascular mortality. The present study indicates that elevated admission level of IL-6 could provide valuable information for long-term risk stratification in patients with STEMI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis — an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420: 868–874
Fichtlscherer S, Heeschen C, Zeiher AM. Inflammatory markers and coronary artery disease (2004). Curr Opin Pharmacol 4: 124–131
Fisman EZ, Benderly M, Esper RJ, Behar S, Boyko V, Adler Y, Tanne D, Matas Z, Tenenbaum A (2006) Interleukin-6 and the risk of future cardiovascular events in patients with angina pectoris and/or healed myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 98:14–18
Yan JC, Zhu J, Gao L, Wu ZG, Kong XT, Zong RQ, Zhan LZ (2004) The effect of elevated serum soluble CD40 ligand on the prognostic value in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Clin Chim Acta 343:155–199
Cavusoglu E, Ruwende C, Chopra V, Yanamadala S, Eng C, Clark LT, Pinsky DJ, Marmur JD (2006) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) is an independent predictor of allcause mortality, cardiac mortality, and myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 151:1101.e1–1101.e8
Blankenberg S, Rupprecht HJ, Poirier O, Bickel C, Smieja M, Hafner G, Meyer J, Cambien F, Tiret L, AtheroGene Investigators (2003) Plasma concentrations and genetic variation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and prognosis of patients with cardiovascular disease. Circulation 107:1579–1585
Yudkin JS, Kumari M, Humphries SE, Mohamed-Ali V (2000) Inflammation, obesity, stress and coronary heart disease: is interleukin-6 the link? Atherosclerosis 148:209–214
Sukhija R, Fahdi I, Garza L, Fink L, Scott M, Aude W, Pacheco R, Bursac Z, Grant A, Mehta JL (2007) Inflammatory markers, angiographic severity of coronary artery disease, and patient outcome. Am J Cardiol 99:879–884
Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP (2000) Myocardial infarction redefined-a consensus document of the Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:959–969
Tan J, Hua Q, Gao J, Fan X (2008) Clinical implications of elevated serum interleukin-6, soluble CD40 ligand, metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Clin Cardiol 31:413–418
Zairis MN, Adamopoulou EN, Manousakis SJ, Lyras AG, Bibis GP, Ampartzidou OS, Apostolatos CS, Anastassiadis FA, Hatzisavvas JJ, Argyrakis SK, Foussas SG, Biomarkers of Inflammation and Outcome in Acute Coronary Syndromes (BIAS) Investigators (2007) The impact of hs C-reactive protein and other inflammatory biomarkers on long-term cardiovascular mortality in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Atherosclerosis 194:397–402
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH (2000) Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation 101: 1767–1772
Koukkunen H, Penttila K, Kemppainen A, Halinen M, Penttila I, Rantanen T (2001) C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the prognostic classification of unstable angina pectoris. Ann Med 33:37–47
Ohtsuka T, Hamada M, Inoue K, Ohshima K, Sujzuki J, Matsunaka T, Ogimoto A, Hara Y, Shigematsu Y, Higaki J (2004) Relation of circulating interleukin-6 to left ventricular remodeling in patients with reperfused anterior myocardial infarction. Clin Cardiol 27:417–420
Funayama H, Ishikawa SE, Kubo N, Yasu T, Saito M, Kawakami M (2006) Close association of regional interleukn-6 levels in the infarct-related culprit coronary artery with restenosis in acute myocardial infarction. Circ J 70:426–429
Lindmark E, Diderholm E, Wallentin L, Siegbahn A (2001) Relationship between interleukin 6 and mortality in patients with unstable coronary artery disease: effects of an early invasive or noninvasive strategy. JAMA 286:2107–2113
Heeschen C, Dimmeler S, Hamm CW, van den Brand MJ, Boersma E, Zeiher AM, Simoons ML, CAPTURE Study Investigators (2003) Soluble CD40L ligand in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 348:1104–1111
Varo N, de Lemos JA, Libby P, Morrow DA, Murphy SA, Nuzzo R, Gibson CM, Cannon CP, Braunwald E, Schonbeck U (2003) Soluble CD40L: risk prediction after acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 108:1049–1052
Inokubo Y, Hanada H, Ishizaka H, Fukushi T, Kamada T, Okumura K (2001) Plasma levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 are increased in the coronary circulation in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J 141:211–217
Derosa G, D’Angelo A, Scalise F, Avanzini MA, Tinelli C, Peros E, Fogari E, Cicero AF (2007). Comparison between metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in healthy subjects, diabetics, and subjects with acute coronary syndrome. Heart Vessels 22:361–370
Fukuda D, Shimada K, Tanaka A, Kusuyama T, Yamashita H, Ehara S, Nakamura Y, Kawarabayashi T, Iida H, Yoshiyama M, Yoshikawa J (2006). Comparison of levels of serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 in patients with acute myocardial infarction versus unstable angina pectoris versus stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 97:175–180
Fujiwara T, Matsunaga T, Kameda K, Abe N, Ono H, Higuma T, Yokoyama J, Hanada H, Osanai T, Okumura K (2007) Nicorandil suppresses the increases in plasma level of matrix metalloproteinase activity and attenuates left ventricular remodeling in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 22:303–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., Hua, Q., Li, J. et al. Prognostic value of interleukin-6 during a 3-year follow-up in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 24, 329–334 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-008-1128-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-008-1128-8