Abstract.
qBackground: In patients with chronic renal failure undergoing long-term hemodialysis, ischemic heart disease accounts for up to 50% of mortality. Cardiac troponins T (TnT) and I (TnI) are frequently elevated in this patient group, but data on the prognostic relevance of these markers, especially TnI, are controversial. The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic power of a new, sensitive TnI assay in comparison with TnT and other cardiac markers.
qPatients and Methods: 104 ambulatory and in-hospital patients (41 women, median age: 65 years, interquartiles: 48–72.5 years; 63 men, median age: 63 years, interquartiles: 51.3–72.5 years) undergoing long-term hemodialysis were investigated. Patients were followed up for 6 months for all kinds of fatal events and nonfatal cardiac events. Serum levels of cardiac TnT, two TnI assays (ACS:180 and Stratus II), CK (creatine kinase), and CK-MB were measured pre- and post-dialysis.
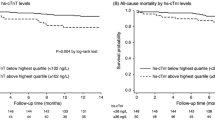
qResults: Pre- and post-dialysis results were not different for TnT and TnI, while CK and CK-MB levels were significantly lower post-dialysis. Elevated (pre-)dialysis levels were found in 65.7% of patients for TnT (> 0.1 μg/l), in 32.4% for TnI (ACS:180, > 0.15 μg/l), in 2.9% for TnI (Stratus II, > 0.4 μg/l), in 5.7% for CK (> 170 U/l), and in 2.8% for CK-MB (> 1.0 μg/l). 6-month events were observed in 42 patients (40.4%; 20 fatal, 22 nonfatal). The relative risk for 6-month events was calculated to be 16.0-fold for TnT and 8.5-fold for a known coronary heart disease, while both TnI and CK-MB did not predict 6-month events independently.
qConclusions: TnT and a known coronary heart disease are relevant, independent risk factors in patients with chronic renal failure undergoing long-term hemodialysis.
Zusammenfassung.
qHintergrund: Ischämische Herzerkrankungen sind für bis zu 50% der Mortalität bei Patienten mit chronischer Niereninsuffizienz unter Langzeitdialyse verantwortlich. Die kardialen Troponine T (TnT) und I (TnI) sind bei diesen Patienten nicht selten erhöht. Die vorliegenden Studiendaten über die prognostische Relevanz sind jedoch, insbesondere für TnI, kontrovers. Ziel dieser Studie war es, die prognostische Aussagekraft eines neuen, sensitiven TnI-Tests im Vergleich zu TnT und anderen Herzmarkern zu untersuchen.
qPatienten und Methodik: 104 ambulante und stationäre Langzeitdialysepatienten (41 Frauen, Median: 65 Jahre, Interquartilbereich: 48-72,5 Jahre; 63 Männer, Median: 63 Jahre; Interquartilbereich: 51,3-72,5 Jahre) wurden untersucht. Bei den Patienten wurden in einem 6-Monats-Zeitraum alle tödlichen Ereignisse sowie nichttödliche kardiale Ereignisse erfasst. Die Serumspiegel von TnT, zwei TnI-Tests (ACS:180 und Stratus II), CK (Kreatinkinase) und CK-MB wurden vor und nach Dialyse bestimmt.
qErgebnisse: Die Serumspiegel von TnT und TnI wurden durch das Dialyseverfahren nicht beeinflusst, während für CK und CK-MB nach Dialyse signifikant niedrigere Werte als vor der Dialyse gefunden wurden. Erhöhte Serumspiegel (vor Dialyse) wurden bei 65,7% der Patienten für TnT (> 0,1 μg/l), bei 32,4% für TnI (ACS:180, > 0,15 μg/l), bei 2,9% für TnI (Stratus II, > 0,4 μg/l), bei 5,7% für CK (> 170 U/l) und bei 2,8% für CK-MB (> 1,0 μg/l) gefunden. 6-Monats-Ereignisse wurden bei 42 Patienten (40,4%; 20 tödliche, 22 nichttödliche) beobachtet. Das relative Risiko für ein 6-Monats-Ereignis wurde für TnT als 16,0fach und für eine bekannte koronare Herzkrankheit als 8,5fach berechnet. Dagegen konnten die beiden TnI-Tests und die CK-MB nicht als unabhängige Risikofaktoren für 6-Monats-Ereignisse identifiziert werden.
qSchlussfolgerungen: TnT und eine bekannte koronare Herzkrankheit sind relevante, unabhängige Risikofaktoren bei Patienten mit chronischer Niereninsuffizienz unter Langzeitdialyse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Manuscript received: 27. 9. 2002. Manuscript accepted: 18. 2. 2003.
Korrespondenzanschrift Dirk Peetz, MD, Institute of Clinical Chemistry, and Laboratory Medicine, Johannes Gutenberg University, Langenbeckstraße 1, 55101 Mainz, Germany, Phone (+49/6131) 17-2632, Fax -6627, e-mail: peetz@zentrallabor.klinik.uni-mainz.de
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peetz, D., Schütt, S., Sucké, B. et al. Prognostic Value of Troponin T,Troponin I, and CK-MBmass in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure. Med Klin 98, 188–192 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00063-003-1243-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00063-003-1243-3