Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this prospective study was to investigate the agreement in findings between ECG-gated CT and transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) in patients with aortic prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE).
Methods
Twenty-seven consecutive patients with PVE underwent 64-slice ECG-gated CT and TEE and the results were compared. Imaging was compared with surgical findings (surgery was performed in 16 patients).
Results
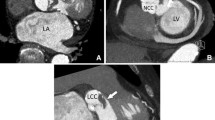
TEE suggested the presence of PVE in all patients [thickened aortic wall (n = 17), vegetation (n = 13), abscess (n = 16), valvular dehiscence (n = 10)]. ECG-gated CT was positive in 25 patients (93 %) [thickened aortic wall (n = 19), vegetation (n = 7), abscess (n = 18), valvular dehiscence (n = 7)]. The strength of agreement [kappa (95 % CI)] between ECG-gated CT and TEE was very good for thickened wall [0.83 (0.62–1.0)], good for abscess [0.68 (0.40–0.97)] and dehiscence [0.75 (0.48–1.0)], and moderate for vegetation [0.55 (0.26–0.88)]. The agreement was good between surgical findings (abscess, vegetation and dehiscence) and imaging for ECG-gated CT [0.66 (0.49–0.87)] and TEE [0.79 (0.62–0.96)] and very good for the combination of ECG-gated CT and TEE [0.88 (0.74–1.0)].
Conclusion
Our results indicate that ECG-gated CT has comparable diagnostic performance to TEE and may be a valuable complement in the preoperative evaluation of patients with aortic PVE.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CM:
-
contrast medium
- ECG:
-
electrocardiogram
- PVE:
-
prosthetic valve endocarditis
- TEE:
-
transoesophageal echocardiography
References
Habib G, Hoen B, Tornos P et al (2009) Guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of infective endocarditis (new version 2009): the Task Force on the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 30:2369–2413
Perrotta S, Aljassim O, Jeppsson A, Bech-Hanssen O, Svensson G (2010) Survival and quality of life after aortic root replacement with homografts in acute endocarditis. Ann Thorac Surg 90:1862–1867
Wang A, Athan E, Pappas PA et al (2007) Contemporary clinical profile and outcome of prosthetic valve endocarditis. JAMA 297:1354–1361
Habib G, Thuny F, Avierinos JF (2008) Prosthetic valve endocarditis: current approach and therapeutic options. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 50:274–281
Chan KL (2002) Early clinical course and long-term outcome of patients with infective endocarditis complicated by perivalvular abscess. CMAJ 167:19–24
Zoghbi WA, Chambers JB, Dumesnil JG et al (2009) Recommendations for evaluation of prosthetic valves with echocardiography and doppler ultrasound: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Task Force on Prosthetic Valves. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22:975–1014, quiz 1082–1014
Birmingham GD, Rahko PS, Ballantyne F 3rd (1992) Improved detection of infective endocarditis with transesophageal echocardiography. Am Heart J 123:774–781
Daniel WG, Mugge A, Grote J et al (1993) Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography for detection of abnormalities of prosthetic and bioprosthetic valves in the mitral and aortic positions. Am J Cardiol 71:210–215
Daniel WG, Mugge A, Martin RP et al (1991) Improvement in the diagnosis of abscesses associated with endocarditis by transesophageal echocardiography. N Engl J Med 324:795–800
Koos R, Mahnken AH, Sinha AM, Wildberger JE, Hoffmann R, Kuhl HP (2004) Aortic valve calcification as a marker for aortic stenosis severity: assessment on 16-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:1813–1818
Stein PD, Yaekoub AY, Matta F, Sostman HD (2008) 64-slice CT for diagnosis of coronary artery disease: a systematic review. Am J Med 121:715–725
Sun Z, Lin C, Davidson R, Dong C, Liao Y (2008) Diagnostic value of 64-slice CT angiography in coronary artery disease: a systematic review. Eur J Radiol 67:78–84
Gilkeson RC, Markowitz AH (2007) Multislice CT evaluation of coronary artery bypass graft patients. J Thorac Imaging 22:56–62
Feuchtner GM, Stolzmann P, Dichtl W et al (2009) Multislice computed tomography in infective endocarditis: comparison with transesophageal echocardiography and intraoperative findings. J Am Coll Cardiol 53:436–444
Li JS, Sexton DJ, Mick N et al (2000) Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 30:633–638
Einstein AJ, Moser KW, Thompson RC, Cerqueira MD, Henzlova MJ (2007) Radiation dose to patients from cardiac diagnostic imaging. Circulation 116:1290–1305
Gahide G, Bommart S, Demaria R et al (2010) Preoperative evaluation in aortic endocarditis: findings on cardiac CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:574–578
Hill EE, Herijgers P, Claus P, Vanderschueren S, Peetermans WE, Herregods MC (2007) Abscess in infective endocarditis: the value of transesophageal echocardiography and outcome: a 5-year study. Am Heart J 154:923–928
Yeter E, Bayram NA, Akcay M, Keles T, Durmaz T (2009) Aortic valve endocarditis with aortic wall thickening requires close follow-up for a possible abscess formation. Perfusion 24:33–35
Walther T, Autschbach R, Falk V et al (1996) The stentless Toronto SPV bioprosthesis for aortic valve replacement. Cardiovasc Surg 4:536–542
Afridi I, Apostolidou MA, Saad RM, Zoghbi WA (1995) Pseudoaneurysms of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: dynamic characterization using transesophageal echocardiographic and Doppler techniques. J Am Coll Cardiol 25:137–145
Tsai IC, Lin YK, Chang Y et al (2009) Correctness of multi-detector-row computed tomography for diagnosing mechanical prosthetic heart valve disorders using operative findings as a gold standard. Eur Radiol 19:857–867
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(MPG 168 kb)
(MPG 272 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagman, E., Perrotta, S., Bech-Hanssen, O. et al. ECG-gated computed tomography: a new role for patients with suspected aortic prosthetic valve endocarditis. Eur Radiol 22, 2407–2414 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2491-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2491-5